Market Share of Open-Source CMS
Distribution of open-source CMS usage in France 1.
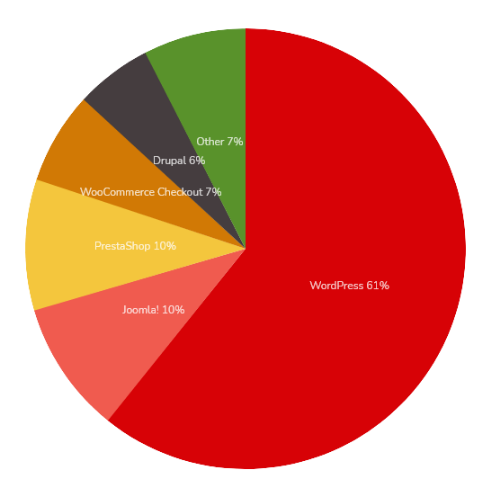
As of October 23, 2021, the website BuiltWith counts 484,190 websites in France using open-source technology.
By definition, these CMSs come with complete freedom in terms of development. Adding functionalities, configuring themes, creating new modules... everything is possible as long as you have some coding knowledge. The code is freely accessible. Their popularity vis-à-vis hosted solutions can be explained by this, not to mention that the possibilities they offer are almost limitless.
They are primarily intended for developers, but enthusiasts can also succeed in creating a functional website thanks to the themes they offer, either paid or free 2.
1. Major Asset: Unlimited Functionalities
Most of the time, they work with a core to which extensions, themes, plugins, and updates can be added, similar to a framework. Many of their functionalities are actually made possible thanks to an immense community of developers who are interested in developing the software because it is also their working tool - when the additions are free - or to integrate with the growth of the CMS and offer a new feature - compatible with it - for sale. For example, WooCommerce, the famous WordPress extension for managing e-commerce on this CMS, was originally created in 2011 by Jigowatt and was then called Jigoshop 3. The core was free, but several other additional services were offered for a fee.
Their capabilities cannot be truly assessed based on the possibilities they offer: their number is almost limitless. What can be taken into account is the effectiveness of the complementary tools and the technologies used, but the question of which open-source CMS is better than another is resolved differently. Instead, one should ask, "In its current state, what is each CMS optimized for?" and inquire whether it can meet the goals one has set.
The great popularity of WordPress is due, in addition to its longevity, to a very intuitive user interface. This is what makes it attractive for enthusiasts, while allowing developers to meet the sometimes demanding requests of their clients.
2. Necessary Evil: A Large Market Share Comes with Great Responsibilities
The major shortcoming of open-source CMSs remains their security vulnerabilities. A software whose entire code is known is a vulnerable software. However, the number of websites worldwide running on such CMSs amounts to 36,255,439, of which 28,183,568 are on WordPress. This would result in significant losses if it were not kept up-to-date by a massive team (805 people contributed to version 5.5 of WordPress, coming from more than 58 different countries 4).
Comparison of infections on open-source CMSs between 2018 and 2019 5.
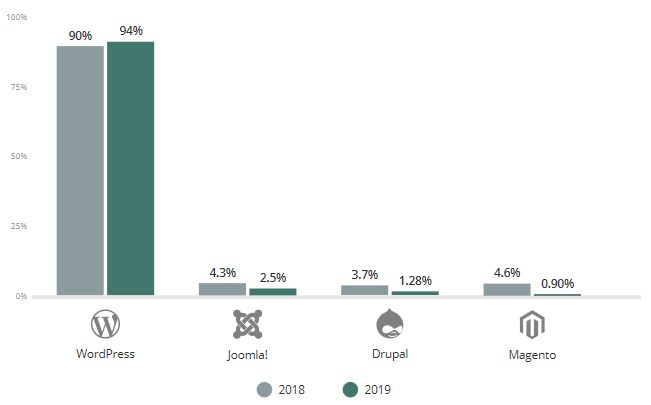
This graph indicates that 94% of security issues are present on websites using WordPress. Its popularity largely contributes to its vulnerability, but the common feature among all these CMSs lies in what makes their strength: their unlimited extension of functionalities.
First and foremost, the core of each of these technologies must, as mentioned, be maintained and evolve over time to fix past vulnerabilities and possibly anticipate future ones.
One must also be able to keep up with the various technologies on which the CMS depends (HTML5, PHP 8...) to remain operational, competitive, and responsive.
Furthermore, these continuous updates can be a source of long and tedious verifications for users on the site using the respective CMS, to ensure that the new upgrade has not disrupted the proper functioning of the site. They often require the intervention of a professional who can navigate through them.
Finally, non-native functionalities also need to be constantly updated to align with each of the aforementioned points, which adds to the manipulations and complicates the task. Thus, a plugin whose development has been discontinued by the developer or the company managing it becomes less recommended because it is vulnerable. Changing it can then require several hours of work and, once again, the intervention of an expert is needed.
Distribution of infections on outdated open-source CMSs 6.
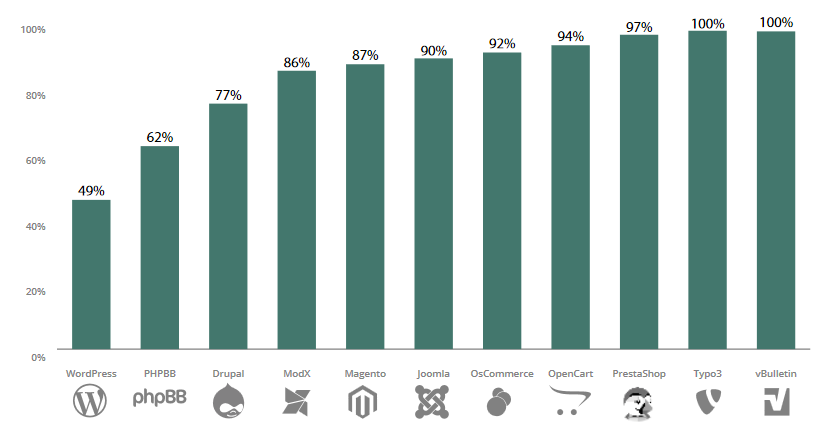
Updating the native code of most CMSs does not happen automatically, which further complicates things for amateur developers. WordPress has implemented it since version 3.7, so it has fewer infections on its older versions than other CMSs.
3. Conclusion on Open-Source CMSs
Open-source CMSs are the best solution for obtaining a flexible, extensible, and fully customizable website. Their free nature can be balanced by the need to seek professional assistance or the time investment required to have a complete website. Security is their main drawback, but a knowledgeable user can avoid its pitfalls.
All these points make these CMSs a good long-term solution for professional websites - and even for individuals - managing low or high traffic: their power makes them a relevant tool for a wide range of websites.
They are especially popular among small and medium-sized businesses 7, due to their relatively lower cost, the evolution possibilities they offer, and the ease of making minor changes to the site.
Annex 1: Technological Comparison of the 7 Most Popular Open-Source CMS
| Wordpress | TYPO3 | Joomla! | Drupal | Contao | Neos | Craft | Grav | Kirby | Bolt | APPOE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category | Blog engine | Enterprise GCMS | Web SCMS | Web SCMS | Web SCMS | Enterprise Content Management System | Mini CMS | Databaseless CMS | Flat file CMS | Mini CMS | Web SCMS |
| License | GNU GPLv2+ | GNU GPLv2+ | GNU GPL v2+ | GNU GPLv2+ | GNU LGPLv3 | GNU GPLv3+ | Proprietary | MIT | Proprietary | MIT | Proprietary |
| Operating System | Platform-independent | Platform-independent | Platform-independent | Platform-independent | Platform-independent | Platform-independent | Platform-independent | Platform-independent | Platform-independent | Platform-independent | Platform-independent |
| Supported Web Servers | Web Server with PHP and MySQL support | Apache, NGINX, MS IIS, Caddy Server | Apache, Nginx, MS IIS | Web Server with PHP support | Web Server with PHP and MySQL support | Apache and NGINX are preferred, others work well too | Apache, NGINX, MS IIS | Apache, NGINX, MS IIS, LiteSpeed, Lightly, etc. | Apache, NGINX | Apache, NGINX | Web Server (Apache, NGINX) with PHP and MySQL support |
| Supported Databases | MySQL, MariaDB | MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, MS SQL Server, SQLite | MySQL, MS SQL Server, PostgreSQL | MySQL, MariaDB, Percona Server, PostgreSQL, SQLite | MySQL | MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, SAP Sybase SQL Anywhere, SQLite, Drizzle | MySQL | ✘ | SQLite, MySQL | SQLite, MySQL, PostgreSQL | MySQL, MariaDB |
| Middleware | PHP | PHP, SQL, JavaScript | PHP | PHP | PHP | PHP | PHP | PHP | PHP | PHP | PHP |
| Template Engine | PHP | TypoScript | PHP | PHP | PHP | Fluid, AFX | Twig | Twig | PHP/HTML | Twig | PHP |
| Extensions and Extension Modules | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Browser-based Backend | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| XML Interface | Only with an extension | Only with an extension | Only with an extension | Only with an extension | Only with an extension | Only with an extension | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | Only with an extension |
| Integration of Custom Scripts | ✔ | ✔ | Only with an extension | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Multi-tenant | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✔ |
| User Grouping, Transmission, and Restriction of Rights | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Multi-level Approval Control | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ |
| Multi-level Workflow | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | Only with an extension | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| WYSIWYG | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Multimedia Elements (Video and Audio Content or Flash Animation) | ✔ | ✔ | Only with an extension | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | Only with an extension | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Blog System | ✔ | Only with an extension | Only with an extension | ✔ | Only with an extension | ✔ | ✔ | Only with an extension | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Spell Checking | ✔ | Only with an extension | Only with an extension | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ |
| Preview Function | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ |
| Multi-language | Only with an extension | ✔ | Only with an extension | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | Only with an extension | ✔ |
| Search Function | ✔ | Only with an extension | Only with an extension | ✔ | ✔ | Only with an extension | ✔ | Only with an extension | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Tagging | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | Only with an extension | Only with an extension | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ |
| Search Engine Friendly URLs | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | Only with an extension | ✔ |
| Manual Entry of Metadata | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | Only with an extension | ✔ | ✔ | Only with an extension | ✔ |
| Possibility of Responsive Web Design | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Documentation | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Tutorials | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
Source: https://www.ionos.fr/digitalguide/hebergement/cms/comparatif-des-meilleurs-cms/ (accessed on 30/10/2021). Forge is our in-house CMS!
Annex 2: Comparison of the Advantages and Disadvantages of the Most Popular Open-Source CMS
| Wordpress | TYPO3 | Joomla | Drupal | Contao | Neos | Craft | Grav | Kirby | Bolt | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Advantages |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Disadvantages |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Source: https://www.ionos.fr/digitalguide/hebergement/cms/comparatif-des-meilleurs-cms/ (page consultée le 30/10/2021)
Annex 3: Performance Comparison for the Most Popular Open-Source CMS
| WordPress | PrestaShop | Joomla! | Drupal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rapidité du logiciel | +++ | ++ | + | + |
| Simplicité d'utilisation | +++ | ++ | ++ | + |
| Adapté pour un site avec une structure simple | +++ | + | + | + |
| Possibilité de personnalisations | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ |
| Bibliothèque d'extensions | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++ |
| Adapté à la création d'un site complexe, avec un fort trafic | ++ | + | ++ | +++ |
| Popularité (téléchargements moyens/semaine) | 1 000 000 | N/A | 113 000 | 34 000 |
| Part sur le marché des CMS | 63.5 % | 3.9 % | 2.6 % | 0.8 % |
| Nombre de thèmes gratuits | + 2 000 | N/A | + 900 | + 1 800 |
| Nombre de plugins gratuits | + 27 000 | + 3 000 | + 7 000 | + 24 000 |
| Fréquence des mises à jour | 42 jours | N/A | 36 jours | 51 jours |
| Niveau de compétences | Amateur | Standard | Standard | Standard |
Source: https://www.ovhcloud.com/fr/web-hosting/uc-cms-comparison/ (accessed on 03/11/2021)
1. Source: builtWith website, https://trends.builtwith.com/cms/open-source/country/France (accessed on 04/11/2021).
2. For an overview of the features, advantages, and disadvantages of different products on the market, refer to the tables in the appendix at the end of the article.
3. Source: https://www.kasareviews.com/jigoshop-review-end-of-jigoshop-ecommerce/ (accessed on November 11, 2021).
4. Source: http://urlr.me/mnzSq (accessed on November 11, 2021).
5. Source: https://sucuri.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/20-sucuri-2019-hacked-report-1.pdf, page 8 (accessed on November 11, 2021).
6. Ibid, page 10.
7. Source (in English) for Worpress: http://urlr.me/87zDH, or Drupal: http://urlr.me/T5FS4.